Mutually Exclusive Events and Overlapping Events
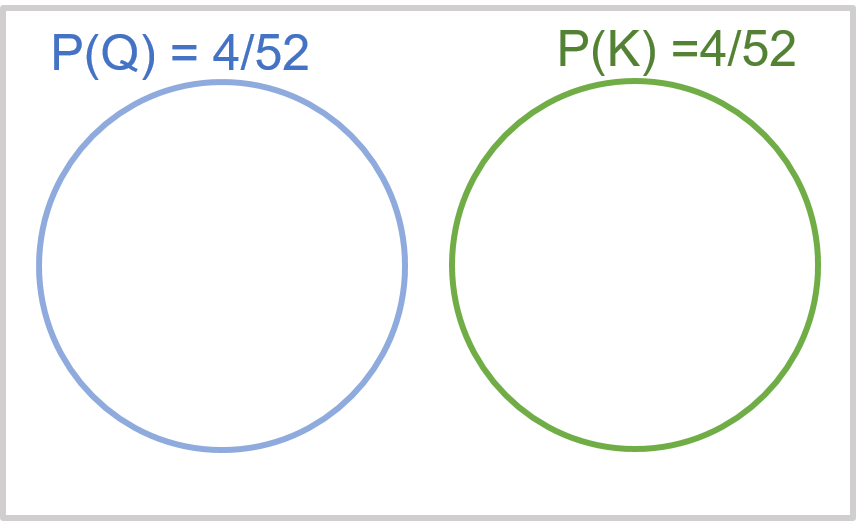
Exhibit 34.3 Mutually exclusive events.
As shown in Exhibit 34.3, the events picking a queen (Q) and picking a king (K)
are mutually exclusive; their range of possible values do not overlap. For such mutually
exclusive events, the probability that either one or the other will occur, is a summation of their
individual probabilities:
$$P(Q \,or \,K) = P(Q) + P(K)$$
The probability that the card is either a queen or a king is 4/52 + 4/52 = 8/52.
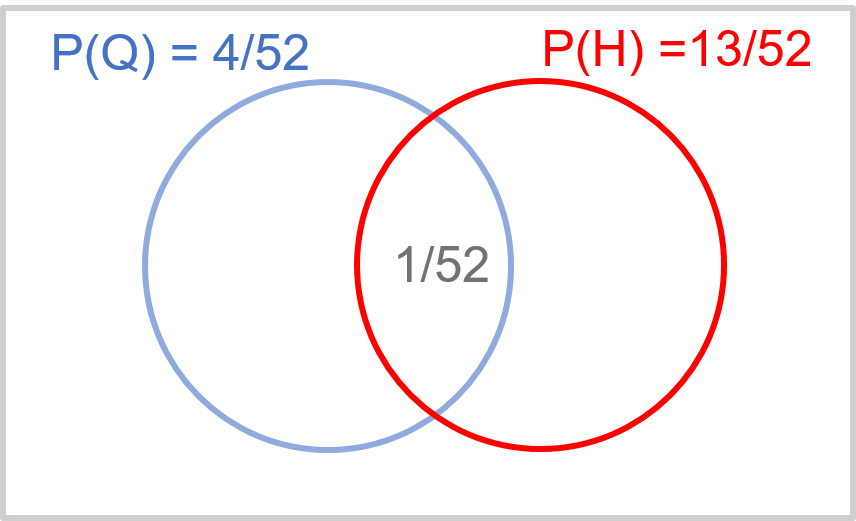
Exhibit 34.4 Events that are not mutually exclusive.
If Q and H are not mutually exclusive events, their range of possible values will
overlap as shown in Exhibit 34.4, and the probability that either will occur is:
$$P(Q \,or \,H) = P(Q) + P(H) - P (Q \,and \,H)$$
The probability that the card is either a queen or a heart is 4/52 + 13/52 – 1/52.