To improve efficiencies, ISPs keep copies of requested
resources on users’ devices. This temporary storage facility, called a cache, stores the served
resources for fixed time duration. (Incidentally, this is why users seeking updated content need
to perform a hard refresh to clear their browser cache to load the most recent version of a
webpage).
While page caching greatly improves the page load speeds, it bypasses the server.
Since no request goes to the server, no log entry is created. This loss of information results in
the under-reporting of metrics such as count of page requests.
It is estimated that caching accounts for as much as a third of all page views. Not
only does this result in the loss of data for web analytics, but it also introduces a bias.
Web analytics based on server logs assumes a fixed or static
IP address. However, this is often not the case for home users. These users are usually assigned
dynamic IP addresses, via Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which can change from time to
time. When this occurs, an existing user assigned a new IP address would be captured as new user,
which artificially inflates the number of new users and deflates the number of repeat users.
Although this occurrence is infrequent, it can cause problems in accurately tracking and analysing
user behaviour.
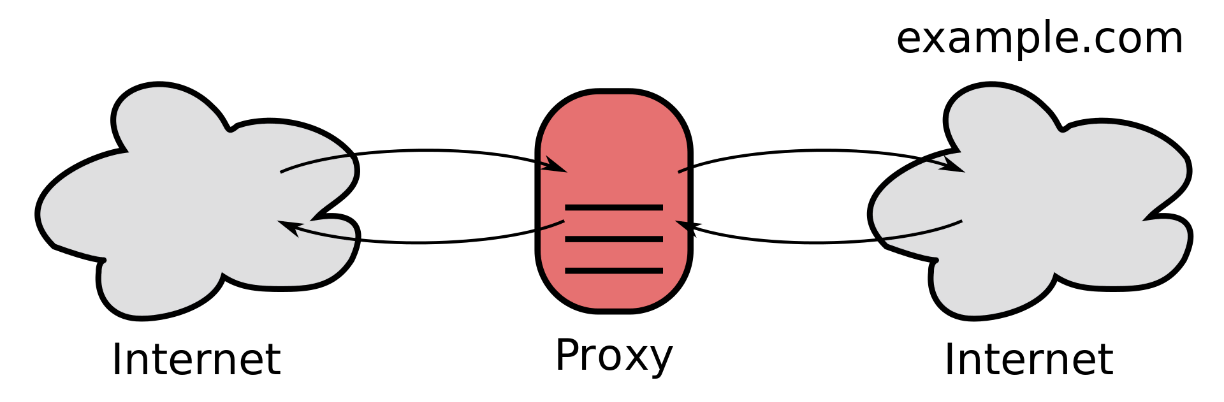

Exhibit 28.2 Proxy server (source Wikipedia).
A proxy server, shown in Exhibit 28.2, acts as an
intermediary for requests from clients seeking pages from the website’s server. In addition to
improving performance, a proxy server also enhances security.
The use of a proxy servers can cause issues for web analytics. Proxy servers
maintain copies of results of users’ requests for a fixed time duration, which means no request
goes from users to the servers hosting the requested resources. Consequently, no log entries are
created at the hosts, which leads to under-reporting of metrics and inaccurate analysis of user
behaviour.
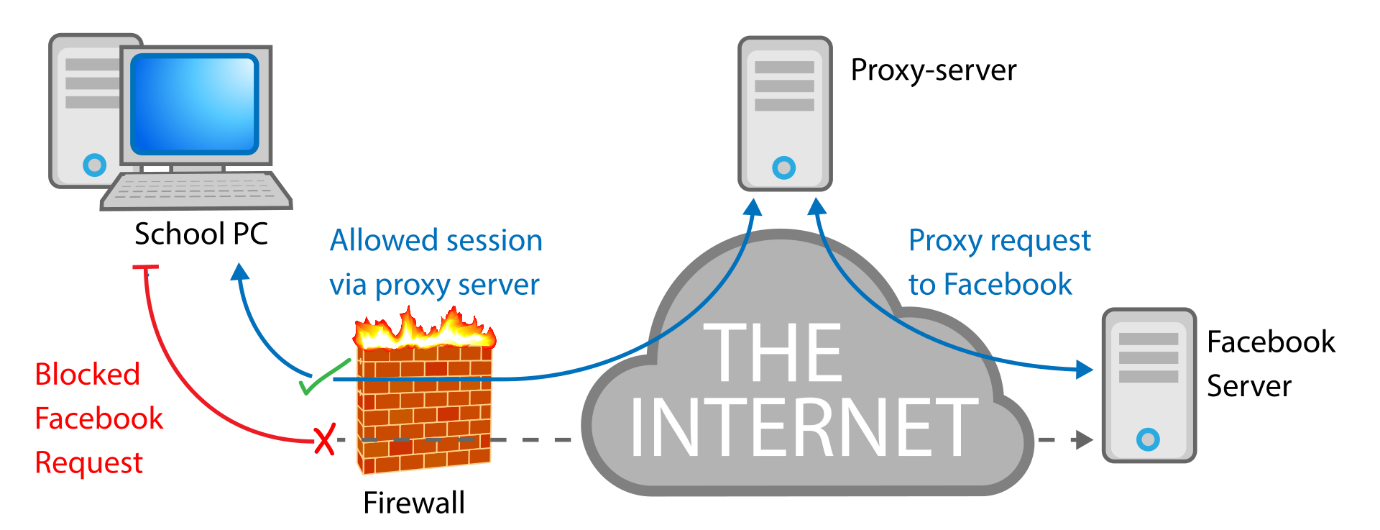
Exhibit 28.3 Proxy server circumvents firewall filter (source Wikipedia).
Proxy servers can be used to bypass filters and censorship.
Although only a small percentage of internet users use circumvention tools, proxies are the most
common means of bypassing government censorship. By using a proxy, a user can access a server that
is restricted using IP-based geolocation.
Exhibit 28.3 illustrates how the circumvention works. In this example, a
firewall blocks requests from the destination to the Facebook server. By routing the request via a
proxy, the user (i.e., School PC) circumvents the firewall and gains access to pages on Facebook.